
The fibula articulates with the tibia laterally at proximal and distal ends however, it has no involvement in weight bearing.Ĭopyright © 2022, StatPearls Publishing LLC. The tibia is a large weight-bearing bone, often referred to as the "shin bone," and articulates with the femoral condyles superiorly and the talus inferiorly. The various muscles of the posterior compartment primarily originate at the two bones of the leg, the tibia, and the fibula. The deep layer of the leg's posterior compartment contains the popliteus, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus, and tibialis posterior muscles. The larger, superficial compartment of the lower leg contains the gastrocnemius, soleus (GS) and plantaris muscles. The posterior compartment of the leg (often referred to as the "calf") further divides into distinct superficial and deep compartments by the transverse intermuscular septum. The posterior compartment musculature functions to plantarflex and invert the foot

The lateral compartment musculature functions to plantar flex and evert the foot Take this anatomy quiz meant for focusing on the anterior side of the thigh. The extensor digitorum longus and extensor hallucis longus also extend the toes. Collectively, they act to dorsiflex and invert the foot at the ankle joint.
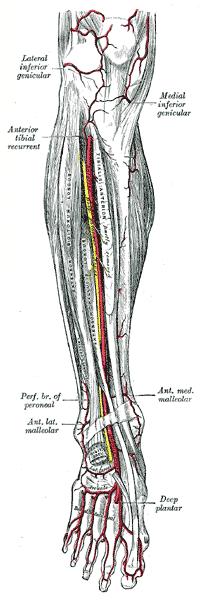
Three major muscles comprise the anterior compartment of the thigh the pectineus, sartorius, and quadriceps femoris. There are four muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg: tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus and fibularis tertius. The anterior compartment musculature functions to primarily dorsiflex the foot and ankle The function of the front compartment of the thigh is to extend the leg at the knee joint. Each compartment contains its distinct set of muscles, vasculature, and innervation: These compartments are formed and separated via divisions by the anterior and posterior intermuscular septa, and the interosseous membrane. The lower leg divides into three fascial compartments:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
